The Redox Engine: How Themarox Supercharges Water’s Oxidative Vitality
The science behind improved Oxidative-Reduction Potential (ORP)—and why balanced oxidation is the secret to cleaner, more resilient water.
How Themarox Enhances Oxidative Balance in Water
Two chapters ago, we learned how Aurmina minerals purify your drinking water by binding suspended particles (flocculation) and causing them to settle out of solution (precipitation).
Aurmina thus removes or renders less active over 250 possible contaminants in your drinking water and, even more importantly, in your store-bought bottled water, the latter of which, in most cases, leads to greater precipitation of excess salts and contaminants than from your municipal water (see the scary photo exhibit of different bottled water brands that me and Lisa put together at the end of Chapter 19: What’s Really in Your Water: The Hidden Crisis Beneath the Surface.
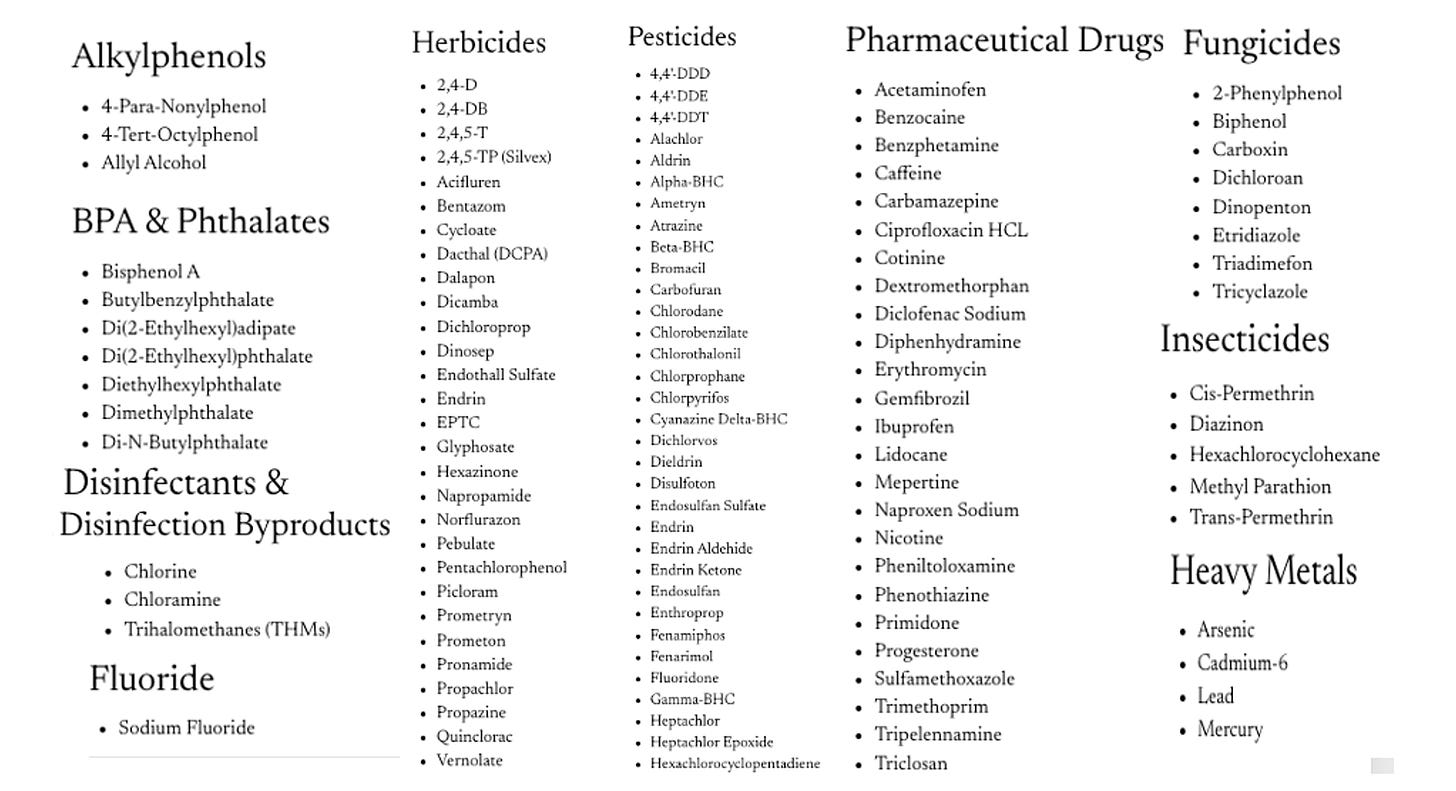
In that chapter, I forgot to put in the actual list of toxins Aurmina removes. So check out the list below, and note that fluoride is on the list for all you lovely “fluoride” obsessives.
Aurmina’s efficacy for neutralizing and removing each compound in the list above is based on rigorous testing by Envirotek Laboratories:
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
OK, we reviewed Aurmina's efficacy in water purification and structuring. Now, let’s investigate the role of oxidation itself in water balance.
One remarkable observation about Themarox and/or Aurmina is their ability to enhance the oxidation–reduction potential (ORP) of water, an important indicator of how effectively a water system can break down or transform organic materials. Although already covered somewhat in earlier chapters, let’s do a deeper dive on “re-dox” reactions. Pumped? Let’s go:
Oxidation vs. Reduction
Electrons are the “currency” of energy.
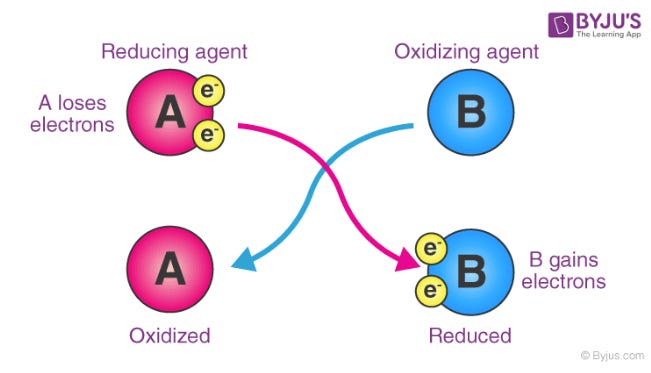
Reactions that move electrons around are what “controls and powers” the functions and processes within chemistry and biologyOxidation = losing electrons.
The molecule or atom loses electrons and becomes more positively charged (or “less negatively charged”).
Mnemonic: OIL = Oxidation Is Loss (of electrons).Oxidizing agent: the taker. It takes electrons from something else (so it gets reduced). I know, it can be hard to get your head around at first.
Reduction = gaining electrons.
The molecule/atom accepts electrons and becomes more negatively charged (or “less positive”).
Mnemonic: RIG = Reduction Is Gain (of electrons).Reducing agent: the giver. It gives electrons to something else (so it gets oxidized). Obviously.
What is ORP?